A debit is an entry into a bookkeeping journal that represents an increase in assets and expenses.
Part of the accounting process for your business activity is understanding that debits and credits help provide insight into your financial statements and reporting and help determine your finances.
Debits vs. credits definition
Accounts use debits and credits to represent the increase and decrease of different accounts.
A debit increases assets and expenses and decreases liabilities, equity, and revenue. A credit increases liabilities, equity, and revenue and decreases assets and expenses.
Keeping track of debits and credits can be tricky, so here is a quick cheat sheet to help:
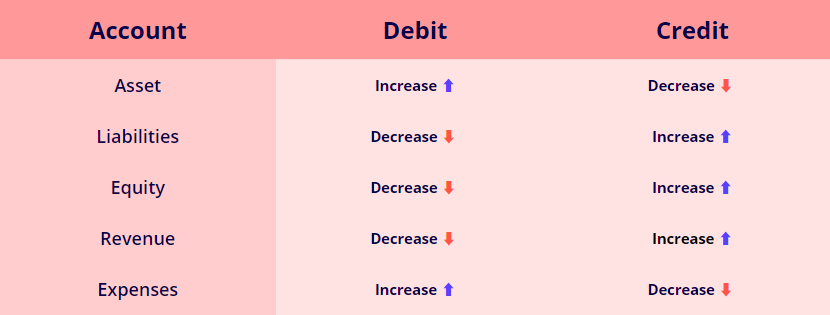
It is essential to know that in double-entry bookkeeping, a transaction affects at least two accounts, and we use debits and credits to show changes resulting from a transaction.
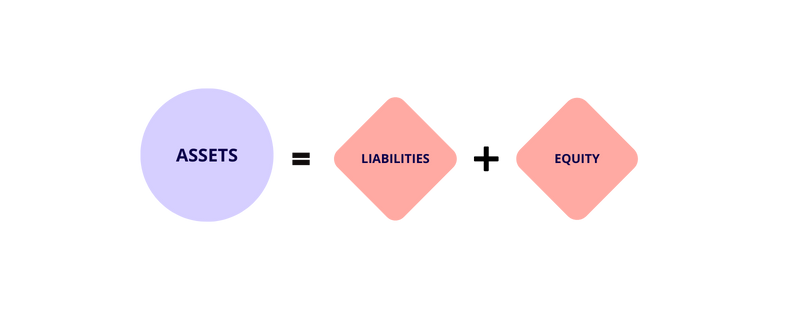
The accounting equation
The “accounting equation” is the foundation of accounting. The formula says a business’s financial position (assets) is the sum of its liabilities and the owner’s equity.
OR
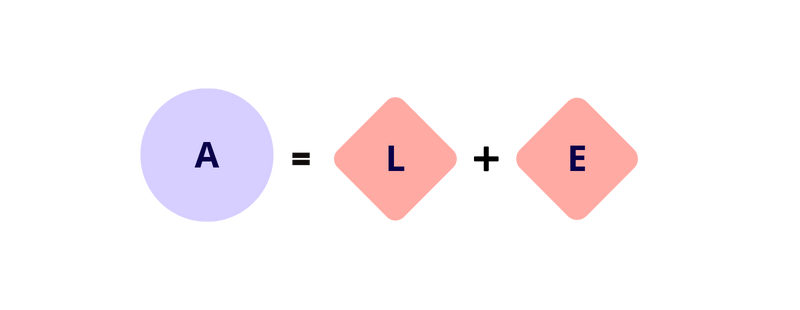
If we expand the equation to better understand a business’s position, we add revenue and expenses to reflect our cheat sheet.
Assets = Liabilities + Equity + (Revenue – Expenses)
These accounts are what hold a business together; using debits and credits together gives us an accurate assessment of our business activities.
Debit Accounts and Credit Accounts
Each account serves a function and it is important to know the difference between them.
Debit accounts
These are found of the left side of the ledger account.

Credit accounts
These accounts are found on the right side ledger account.

Once we understand debits and credits, we can apply them with a journal entry. For simplicity, we will ignore GST in this example.
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01/03/2024 | Inventory | 10,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 10,000 |
The above example shows that the monetary value of inventory (an asset) is a debit entry of $10,000 on the left-hand side of the ledger. We also see the money value is credited to accounts payable (a liability) on the right side of the ledger. It is important to note that your debits and credits must balance.
The example also shows the fundamental nature of accounting and operating a business. An asset is what a company owns and is an economic benefit. A liability is what a business owes in debt and has obligations to pay now or in the future.
Journal entries show the culmination of business activities and transactions for each ledger account. When these are accurately recorded, various reports and statements can be extracted for your financial accounting, such as:
- trial balance
- balance sheet
- cash flow statement
- income statement
It is helpful to keep in mind that debits and credits are a basic function that is fundamental to accounting and bookkeeping. The function of debits and credits ultimately contribute to the larger picture of the overall health of your business and it’s operation.
See related terms
What is an expense?
What are fixed assets?
What is a balance sheet?