‘Expense’ is one of the most fundamental terms in finance, business, and accounting. While it may seem straightforward, there are several intricacies around the term, and if you’re going into business—or undertaking bookkeeping or accounting—your knowledge of what an expense is, and how it works needs to be sound.
Expense (meaning)
An expense is a cost incurred or payment made for goods, services, or resources to support a business. Expenses are typically associated with revenue generation or day-to-day operations.
Expenses are subtracted from revenue to calculate profit.
There are many types of expenses in the business world. Let’s unpack the most important.
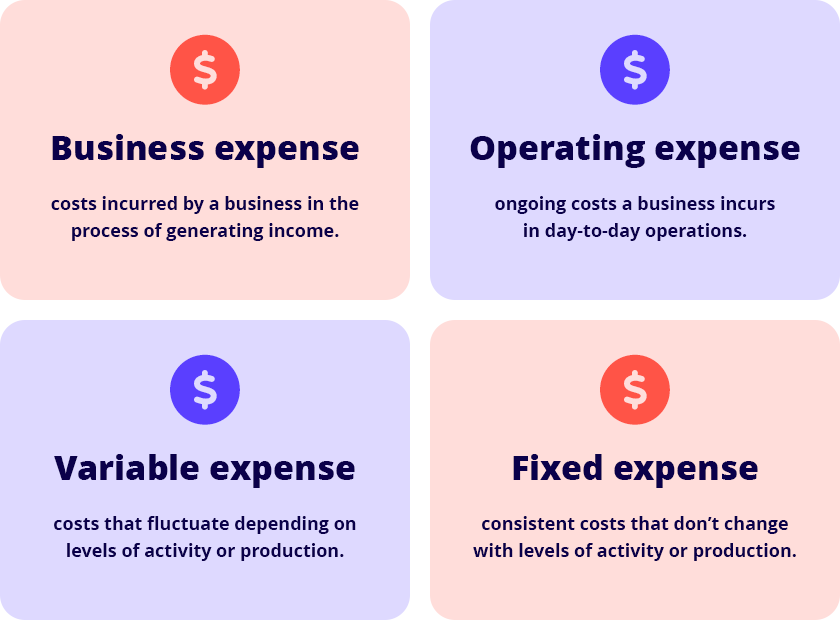
1. Business expense
A business expense refers to the costs incurred by a business in the process of generating income. A business expense must be kept separate from your own expenses.
Businesses need to keep accurate records of their business expenses for tax purposes and sound financial management. Software to help you manage your business expenses can assist you here.
Common business expenses include:
- operating expenses
- employee expenses
- cost of goods sold (COGS)
- marketing and advertising
- travel and accommodation
- professional fees
- depreciation
- interest
- taxes.
2. Operating expense
Operating expenses are the ongoing costs a business incurs in day-to-day operations to generate revenue. Importantly, COGS or expenses outlaid in the direct production of goods, are not included in operating expenses.
Operating expenses can include:
- rent
- salaries
- utilities
- marketing
- maintenance.
To calculate your ‘operating profit’, deduct your operating expenses from your revenue.
3. Variable expense
Variable expenses are costs that fluctuate in terms of a business’s level of activity or production. If you produce more, variable expenses go up; if you produce less, they go down.
Examples of variable expenses include:
- raw materials
- direct labour
- utilities.
Variable expenses differ from fixed expenses in terms of their changing nature.
4. Fixed expense
Unlike variable expenses, fixed expenses don’t fluctuate. Fixed expenses are consistent costs that don’t change with a business’s level of activity or production.
Examples of fixed expenses include:
- rent
- salaries
- insurance
- fixed billing like phone and internet.
5. Capital expense
Capital expenses are spent on purchasing, maintaining, or improving property or assets. Capital expenses are usually paid toward long-term investments over more than a year.
Examples of capital expenses include:
- property
- vehicles
- computers
- equipment
- furniture.
See related terms
What is a ledger?
What is cash flow?
What are fixed assets?