Tax deductions are allowable expenses that you can claim with the ATO to reduce your taxable income.
Claiming a tax deduction with the ATO (while filing a tax return) reduces your taxable income which generally leads to you paying less tax.
As a business owner or individual, the aim of the game is to reduce your taxable income as much as is legally allowable to keep more money in your pocket (aka, more gross profit.)
Examples of tax deductions
Generally, you can deduct expenses that are used for the sole purpose of ‘doing the work’ of your employment or business. The work-related expenses you claim must relate directly to your business operations and revenue generation.
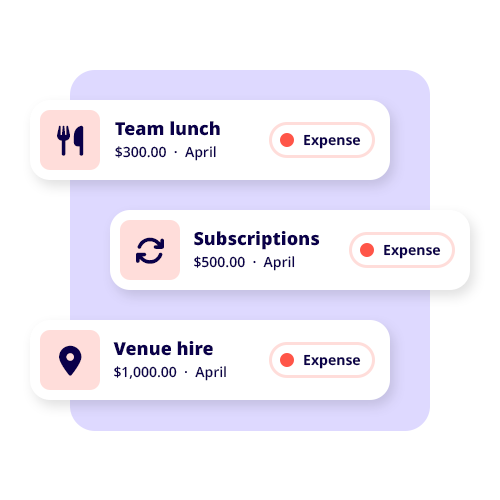
Some examples include, but are not limited to:
- Home office expenses.
- Work vehicle expenses.
- Equipment and device expenses.
- Digital product expenses.
- Operating expenses.
- Depreciation of equipment.
- Employee’s wages.
- Repairs and maintenance.
For more complete and thorough information about allowable tax deductions on what you’re able to claim, always refer to the ATO website.
Keeping records of your expenses
Whenever you claim an expense for tax deduction purposes, you must be able to provide proof of purchase for the expense in question and know that the expense is indeed allowable (by the ATO).
Be sure you retain all receipts and invoices that pertain to the expenses you’re claiming ideally electronically or within your accounting software. When you claim a deduction, you must back it up with evidence. You cannot claim on tax without receipts.
Tax deduction advice
Assessing tax deductions and allowable expenses can be a tricky affair. There are a lot of grey areas and specificities when it comes to accurately identifying and claiming such expenses.
To be sure you aren’t erroneously claiming invalid work-related deductions or overlooking allowable deductions, come tax time, it’s always prudent to enlist a registered tax agent or qualified accountant. They can professionally assess your tax return to ensure your claims are complete and without error.
See related terms
What are fixed assets?
Gross profit vs net profit
What is a sole proprietorship?